

What we do
The challenge
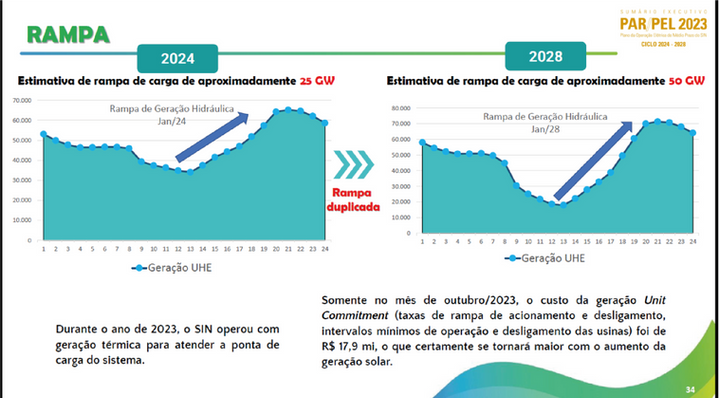
Meet the evolution of net load ramps throughout the day, expected to reach 50 GW in 2028, as shown in the figures below.

Solution
The flexible hydroelectric plants developed by H2Way were designed to operate daily, both in reducing the downward slope operating as load, and the upward slope operating as generation.
Energy storage through Pumped Storage Plants (UAB)
UABs - Pumped Storage Plants are reversible hydroelectric plants with a daily cycle and closed or semi-closed circuit.
UABs do not compete with the Hydroelectric Power Plants (UHEs) of the Brazilian Electric System, and have superior capacity and operational flexibility compared to them, thermal plants and conventional batteries.
The H2WAY PRODUCT was developed to perform specific functions in the Brazilian Electrical System, and has the following basic characteristics:
Installed Power greater than 400 MW.
Limited use of water resources.
Short project implementation deadlines (3 to 5 years).
Minimization of environmental impacts with the use of existing and/or new reservoirs with an extremely reduced flooded area in relation to the project's capacity.
Locational signal differentiated by its proximity to cargo and consumption centers in the southeast region.
What we have already done:
• We have identified a series of unique ventures that would have maximum implementation competitiveness and that can now be developed together with interested investors under a confidentiality agreement.
• We have built a pipeline of projects for which we are seeking to make viable through participation in the next Capacity Auctions.
• We have built a pipeline of pumped storage projects, which can now be developed together with interested investors, under a confidentiality agreement.

H2Way Portfolio


H2Way Product

Pumped Storage Plants (UAB) are reversible hydroelectric plants with a daily cycle and closed or semi-open circuit. How it works:
• Pumps water from the lower reservoir to the upper one, during periods of lower demand, taking advantage of the system's excess generation to store energy;
• Generates energy by discharging water from the upper reservoir to the lower reservoir during the system's greatest need.
